Cutting-Edge Technology in Dermatology: The Impact of 3D Printing on Skin Grafts
- Simone L

- Apr 23, 2024
- 3 min read

The field of dermatology is continuously evolving, with new technologies transforming how skin conditions are treated and managed. One of the most exciting advancements is the use of 3D printing to create custom skin grafts, a development that holds significant promise for patients with severe burns, chronic wounds, and other skin injuries.
The Promise of 3D-Printed Skin Grafts:
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, allows for the creation of complex structures layer by layer, making it possible to produce skin grafts that closely mimic the patient’s own skin in terms of texture, elasticity, and color.
This technology offers several key advantages:

Customization:
3D printing enables the creation of skin grafts that are tailored to the specific needs of each patient. This customization ensures a better fit and integration with the surrounding tissue, leading to improved healing outcomes.
Speed:
Traditional methods of skin grafting can be time-consuming, often requiring weeks or months to prepare suitable grafts. In contrast, 3D printing can produce grafts rapidly, significantly reducing the time patients spend waiting for treatment.
Reduced Rejection Risk:
By using a patient’s cells to create the grafts, the risk of immune rejection is minimized. This approach also promotes more natural and effective healing, as the body is less likely to react negatively to the implanted tissue.
Recent Developments:
Researchers and companies around the world are making significant strides in the development of 3D-printed skin grafts. For example, a team at the University of Toronto has developed a handheld 3D skin printer that can print sheets of skin tissue directly onto a wound. This portable device uses bio-ink composed of the patient’s cells, ensuring a high degree of compatibility and reducing the risk of rejection.
In another breakthrough, the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine has created a bioprinter capable of printing skin directly onto burn wounds. This bioprinter uses a mix of cells, including fibroblasts and keratinocytes, to produce a structure that closely resembles natural skin. Early trials have shown that this method can significantly speed up the healing process and reduce scarring.
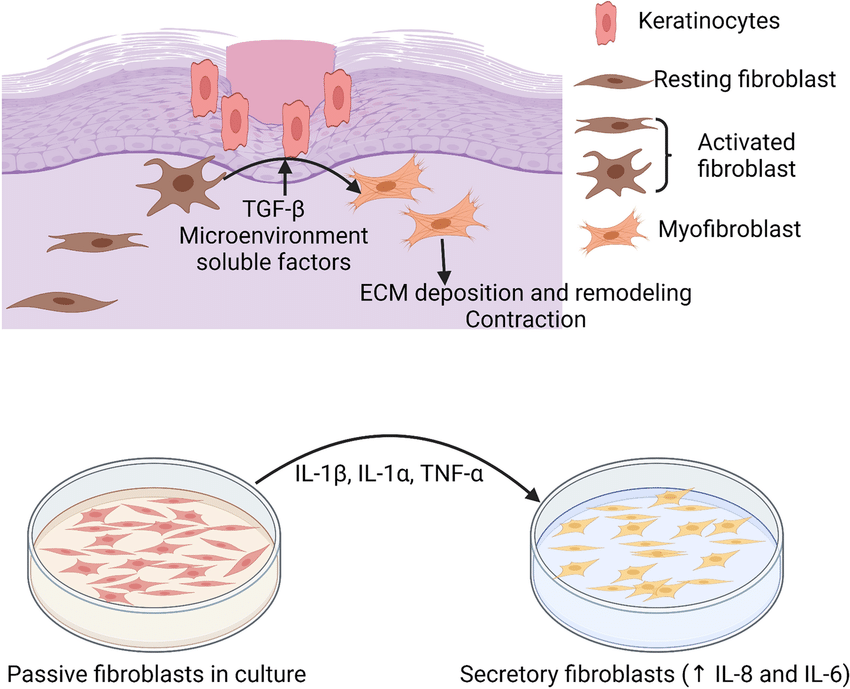
The Future of 3D-Printed Skin Grafts
As research and technology continue to advance, the potential applications for 3D-printed skin grafts are expanding. Future developments may include:
Complex Tissue Structures:
Advances in bioprinting technology could enable the production of skin grafts with complex structures, including hair follicles and sweat glands, enhancing their functionality and appearance.
Integration with Smart Technology:
Incorporating sensors and other smart technologies into 3D-printed skin grafts could allow for real-time monitoring of the healing process, providing valuable data to healthcare providers and ensuring optimal care.
Wider Accessibility:
As the cost of 3D printing technology decreases and techniques become more refined, these advanced skin grafts could become more widely available, benefiting a larger number of patients worldwide.
Conclusion:
The use of 3D printing in dermatology represents a significant leap forward in the treatment of skin injuries and conditions. By enabling the rapid and customized production of skin grafts, this technology has the potential to improve patient outcomes and revolutionize dermatological care. As research continues and new innovations emerge, the future of 3D-printed skin grafts looks incredibly promising, offering hope and healing to patients around the globe.
Citations:
Images:
3D- Printed Skin Grafts: Photo Credit due to IFLScience, asked for permission to use photo, no changes were made to the image.
Fibroblasts and Keratinocytes in Wound Healing: Photo Credit due to ResearchGate, asked for permission to use photo, no changes were made to the image.
Sources:
University of Toronto: https://www.utoronto.ca/news/u-t-researchers-handheld-3d-skin-printer-helps-heal-large-severe-burns-study-finds
Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine: https://school.wakehealth.edu/research/institutes-and-centers/wake-forest-institute-for-regenerative-medicine/awards-honors-and-media-coverage/mobile-bedside-bioprinter-can-heal-wounds#:~:text=Wake%20Forest%20Institute%20for%20Regenerative,printed%20directly%20into%20a%20wound.
763 views

Comments